本文介绍了58同城迁移到AndroidX实践过程及对Jetifier源码分析。
《春宵》
春宵一刻值千金,花有清香月有阴。
歌管楼台声细细,秋千院落夜沉沉。
-宋代,苏轼

前言
AndroidX是谷歌在2018年IO大会上推出的,是对support库的整理后的产物,用于取代support库,解决使用support库必须保持统一的版本及命名混乱等问题。在2018年9月发布了support库的最后一个版本28.0.0,之后support库将不再维护。AndroidX 1.0.0版本对应于support库28.0.0版本。为了确保迁移过程顺畅,迁移前请先将support库升级28.0.0版本。
开始迁移
使用Android Studio提供的功能Refactor > Migrate to AndroidX进行迁移。首先会弹出一个对话框,提示你备份工程代码,并告知可能需要手动处理一些错误。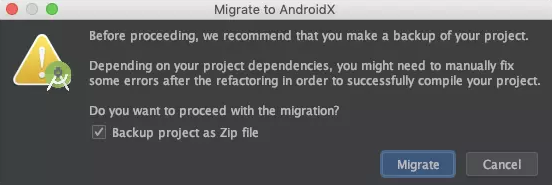
点击Migrate后Android Studio会对工程中所有文件进行搜索需要处理的文件列表,点击Do Refactor开始迁移。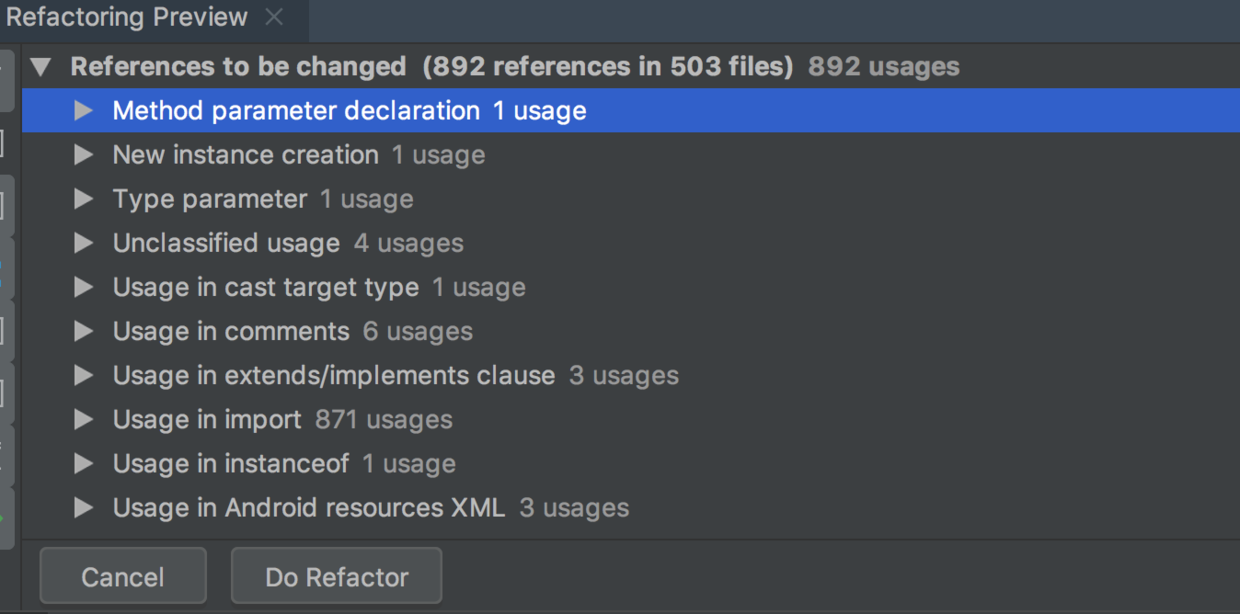
这会在gradle.properties文件中添加以下属性:1
2android.useAndroidX=true //表示启用androidx
android.enableJetifier=true //会对依赖库进行迁移
迁移后效果类似下面的修改:
尝试编译发现有很多错误,有导包错误,搜索发现还有好多文件未能成功迁移: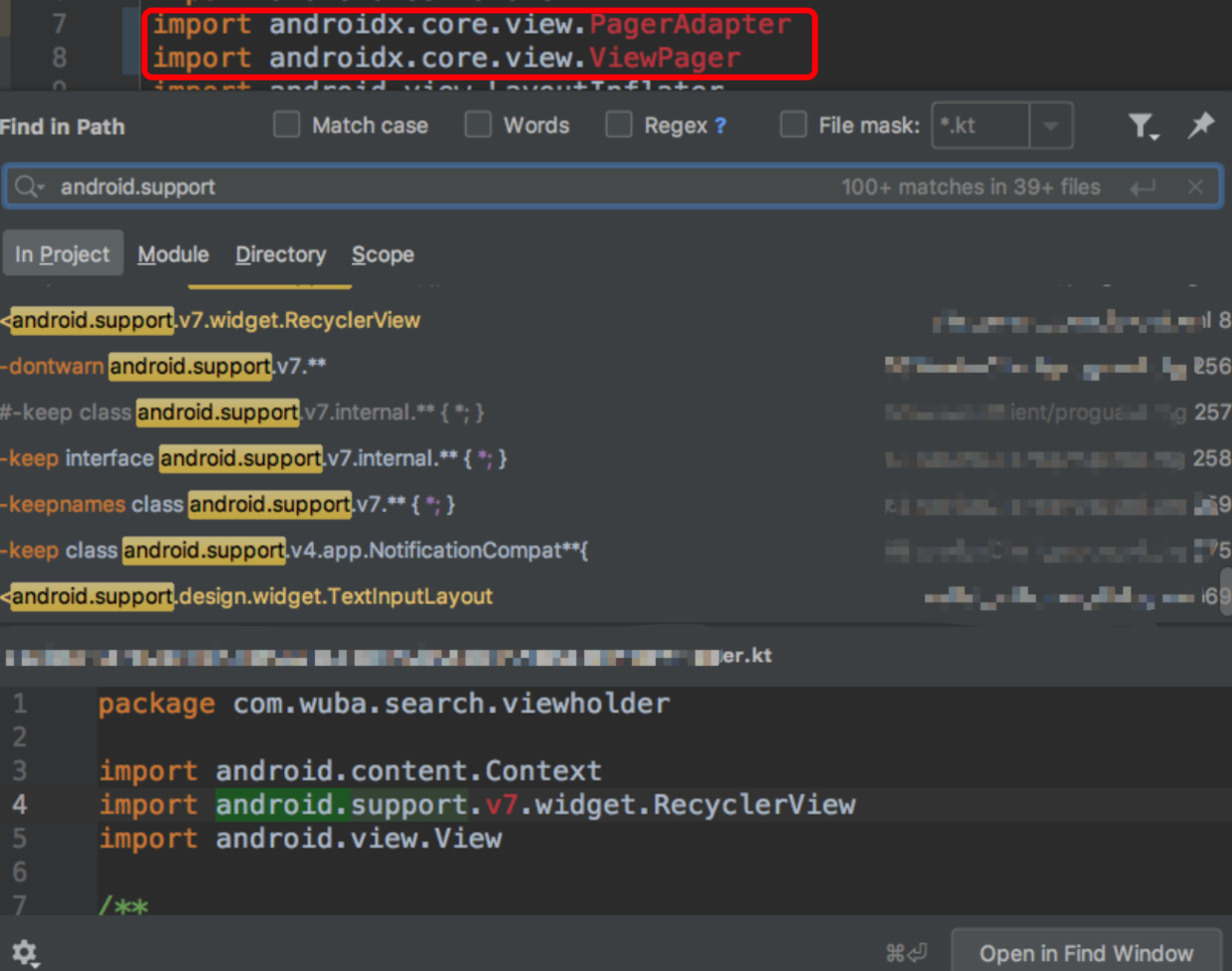
自动化迁移
显然Android Studio提供的工具还有很大的缺陷,由于58同城源码工程代码文件庞大且包含多个业务线,如果手动修改这些导包错误花费的时间成本比较大,并且官方提供了support库和androdx库类映射关系,所以这里我们使用python脚本获取映射关系,通过映射关系对工程中所有文件进行扫描迁移。备注:该脚本不支持多行替换和依赖替换。
在gradle.properties文件中添加以下属性:1
2android.useAndroidX=true //表示启用androidx
android.enableJetifier=true //会对依赖库进行迁移
打开终端在工程根目录执行以下命令:1
2git clone git@github.com:yuweiguocn/MigrateToAndroidX.git
python MigrateToAndroidX/migrate.py
运行结果: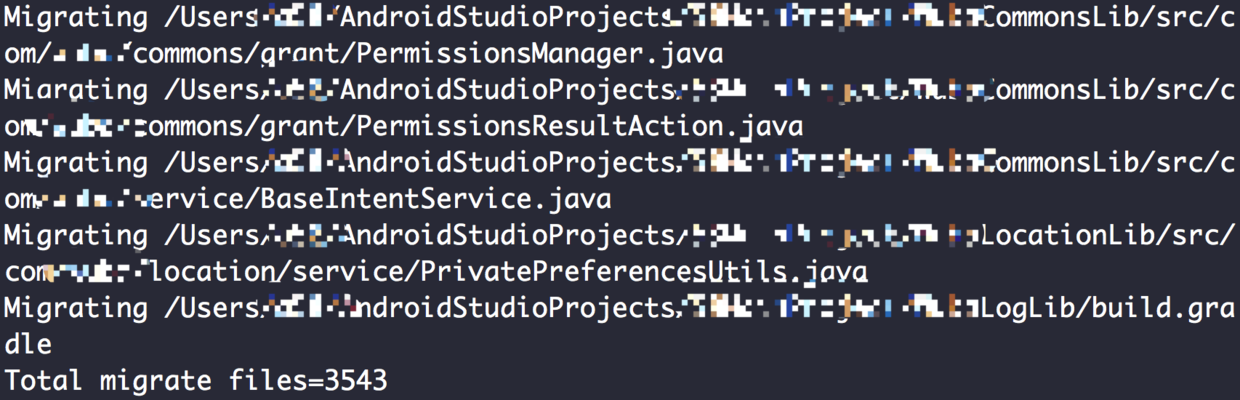
通过此脚本工具迁移后执行打包只出现了一两个小问题,其中一个是使用的butterknife需要升级。从实践结果来看使用脚本工具对源码迁移成本还是相对很低的,并且目前androidx的多个库已经发布了新的版本,所以还没有迁移到androidx的小伙伴是时候进行迁移了。
验证迁移结果
执行混淆打包后查看混淆后的mapping文件,全局搜索android.support发现有800多处,经过确认是androidx库版本带有的support包名的class文件,分别是: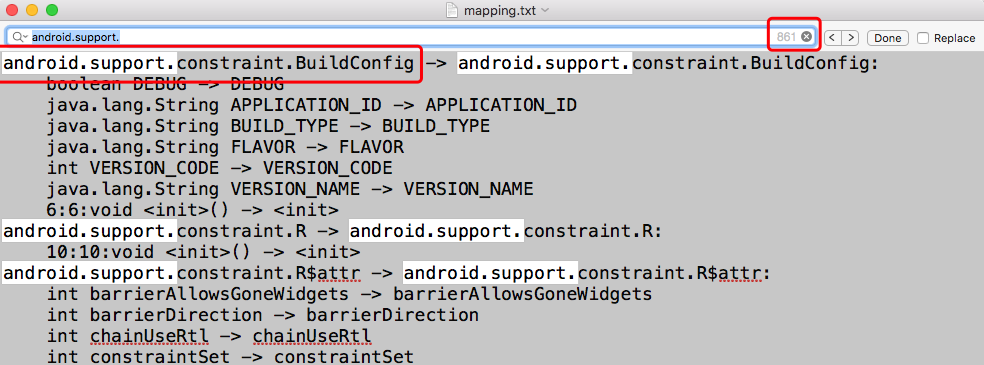
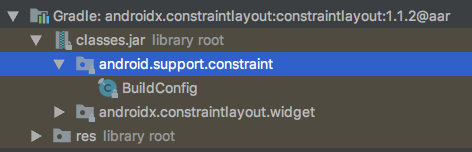
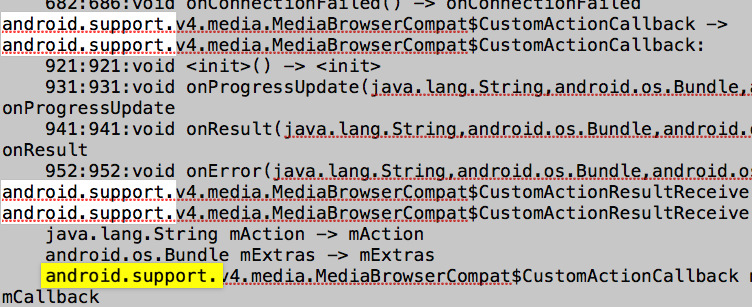
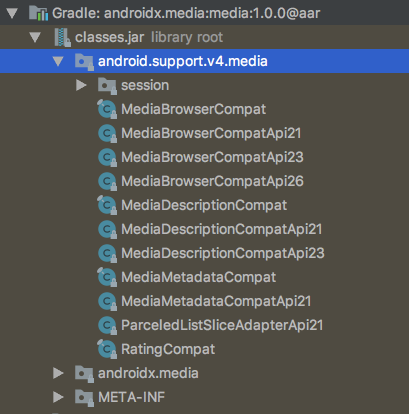
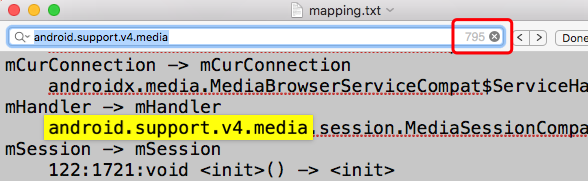
这样可以确认迁移androidx已经完成,最后来看下support库和androidx库的版本对比,确保迁移后不会对现有功能产生影响。
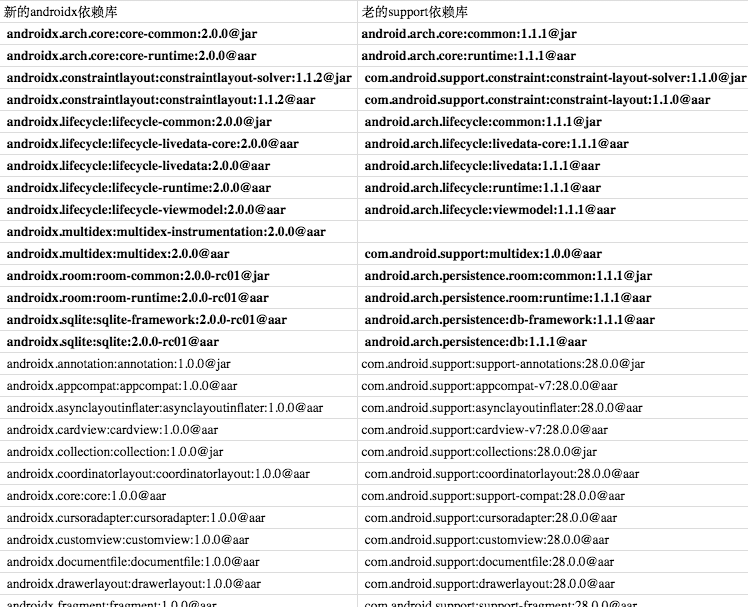
除了黑色加粗的依赖有版本升级其余库均没有版本变动,从官方网站查看版本变更记录:
- arch:没有变更说明
- constraintlayout:没有变更说明,小版本升级影响不大
- lifecycle:修复ProGuard规则
- multidex:修复了与 Robolectric 测试的兼容性问题。提升了版本检查代码的性能。
- room:问题修复及api变更
- sqlite:没有变更说明
重点测试以上依赖库对应的相应功能即可。
Jetifier源码分析
当我们在gradle.properties文件中添加android.enableJetifier=true属性开启Jetifier后执行打包时会自动将依赖库改为新的androidx库,这个是如何做到的?接下来我们对Jetifier的相关源码进行一下分析。备注:基于android插件gradle_3.4.0版本。
Android Gradle插件源码
相关源码可以从这里获取:https://github.com/yuweiguocn/build-system
一个工程中的Module可能包括application和library,这里我们只分析application插件。1
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
从应用的插件名称找到插件配置文件com.android.application.properties,可以看到实现类是AppPlugin。1
implementation-class=com.android.build.gradle.AppPlugin
AppPlugin的父类继承自BasePlugin,BasePlugin最终会在插件apply时调用到VariantManager的createAndroidTasks方法,该方法最终会调用到configureDependencies方法,接下来该主角登场了:
VariantManager.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43public void configureDependencies() {
final DependencyHandler dependencies = project.getDependencies();
// 如果开启了Jetifier没有开启androidX会抛出异常
if (!globalScope.getProjectOptions().get(BooleanOption.USE_ANDROID_X)
&& globalScope.getProjectOptions().get(BooleanOption.ENABLE_JETIFIER)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"AndroidX must be enabled when Jetifier is enabled. To resolve, set "
+ BooleanOption.USE_ANDROID_X.getPropertyName()
+ "=true in your gradle.properties file.");
}
// 如果开启了Jetifier会使用AndroidX替换support
if (globalScope.getProjectOptions().get(BooleanOption.ENABLE_JETIFIER)) {
AndroidXDepedencySubstitution.replaceOldSupportLibraries(project);
}
final String jetifierBlackList =
Strings.nullToEmpty(
globalScope.getProjectOptions().get(StringOption.JETIFIER_BLACKLIST));
dependencies.registerTransform(
transform -> {
transform.getFrom().attribute(ARTIFACT_FORMAT, AAR.getType());
transform.getTo().attribute(ARTIFACT_FORMAT, TYPE_PROCESSED_AAR);
if (globalScope.getProjectOptions().get(BooleanOption.ENABLE_JETIFIER)) {
transform.artifactTransform(
JetifyTransform.class, config -> config.params(jetifierBlackList));
} else {
transform.artifactTransform(IdentityTransform.class);
}
});
dependencies.registerTransform(
transform -> {
transform.getFrom().attribute(ARTIFACT_FORMAT, JAR.getType());
transform.getTo().attribute(ARTIFACT_FORMAT, PROCESSED_JAR.getType());
if (globalScope.getProjectOptions().get(BooleanOption.ENABLE_JETIFIER)) {
transform.artifactTransform(
JetifyTransform.class, config -> config.params(jetifierBlackList));
} else {
transform.artifactTransform(IdentityTransform.class);
}
});
...
}
该方法中判断如果开启了Jetifier会对工程中依赖进行处理,然后注册了JetifyTransform用于处理aar和jar文件。接下来看下对工程中的依赖的处理:
AndroidXDepedencySubstitution.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79object AndroidXDepedencySubstitution {
/**
* 老的依赖到AndroidX依赖的映射
* map中的key是"old-group:old-module" (不包含版本) value是
* "new-group:new-module:new-version" (包含版本).
*/
@JvmStatic
val androidXMappings: Map<String, String> = Processor.createProcessor3(
config = ConfigParser.loadDefaultConfig()!!,
dataBindingVersion = Version.ANDROID_GRADLE_PLUGIN_VERSION
).getDependenciesMap(filterOutBaseLibrary = false)
@JvmStatic
fun replaceOldSupportLibraries(project: Project) {
project.dependencies.components.all { component ->
component.allVariants { variant ->
variant.withDependencies { metadata ->
val oldDeps = mutableSetOf<DirectDependencyMetadata>()
val newDeps = mutableListOf<String>()
metadata.forEach { it ->
val newDep = if (bypassDependencySubstitution(it)) {
null
} else {
androidXMappings["${it.group}:${it.name}"]
}
if (newDep != null) {
oldDeps.add(it)
newDeps.add(newDep)
}
}
// 某些情况下 metadata.removeAll(oldDeps) 不起作用,所以使用循环处理
for (oldDep in oldDeps.map { it -> "${it.group}:${it.name}" }) {
metadata.removeIf { it -> "${it.group}:${it.name}" == oldDep }
}
for (newDep in newDeps) {
metadata.add(newDep)
}
}
}
}
project.configurations.all { config ->
// 只处理可解决的配置
if (config.isCanBeResolved) {
config.resolutionStrategy.dependencySubstitution.all { it ->
maybeSubstituteDependency(it, config, androidXMappings)
}
}
}
}
/**
* 如果依赖是老的support库则使用新的androidx替换
*/
private fun maybeSubstituteDependency(
dependencySubstitution: DependencySubstitution,
configuration: Configuration,
androidXMappings: Map<String, String>
) {
// 只处理 Gradle module 依赖 (group:module:version这种形式的)
if (dependencySubstitution.requested !is ModuleComponentSelector) {
return
}
val requestedDependency = dependencySubstitution.requested as ModuleComponentSelector
if (bypassDependencySubstitution(requestedDependency, configuration)) {
return
}
androidXMappings[requestedDependency.group + ":" + requestedDependency.module]?.let {
dependencySubstitution.useTarget(
it,
BooleanOption.ENABLE_JETIFIER.name + " is enabled"
)
}
}
...
}
AndroidXDepedencySubstitution文件中有一个androidXMappings变量存储的是support依赖和AndroidX依赖之间的映射,key是”old-group:old-module” (不包含版本) ,value是”new-group:new-module:new-version” (包含版本),通过该映射关系对现有工程依赖进行替换。这里用到了Processor类,该类在jetifier工程中,稍后再分析该依赖配置是怎么获取的。
接下来看下刚才注册的JetifyTransform类:
JetifyTransform.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75class JetifyTransform @Inject constructor(blackListOption: String) : ArtifactTransform() {
companion object {
private val jetifierProcessor: Processor by lazy {
Processor.createProcessor3(
config = ConfigParser.loadDefaultConfig()!!,
dataBindingVersion = Version.ANDROID_GRADLE_PLUGIN_VERSION,
allowAmbiguousPackages = false,
stripSignatures = true
)
}
}
private val jetifierBlackList: List<Regex> = getJetifierBlackList(blackListOption)
private fun getJetifierBlackList(blackListOption: String): List<Regex> {
val blackList = mutableListOf<String>()
if (!blackListOption.isEmpty()) {
blackList.addAll(Splitter.on(",").trimResults().splitToList(blackListOption))
}
// Jetifier should not jetify itself (http://issuetracker.google.com/119135578)
blackList.add("jetifier-.*\\.jar")
return blackList.map { Regex(it) }
}
override fun transform(aarOrJarFile: File): List<File> {
Preconditions.checkArgument(
aarOrJarFile.name.toLowerCase().endsWith(".aar")
|| aarOrJarFile.name.toLowerCase().endsWith(".jar")
)
/*
* aars 或 jars 可以分为四类
* - AndroidX 库
* - 老的 support 库
* - 黑名单中的其他库
* - 非黑名单中的其他库
* 下面会相应处理这些情况
*/
// 情况 1: 是AndroidX library不需要处理
if (jetifierProcessor.isNewDependencyFile(aarOrJarFile)) {
return listOf(aarOrJarFile)
}
// 情况 2:如果是老的support库表示在之前的依赖替换阶段没有被替换,可能它还没有androidx版本
// 也不需要对它处理
if (jetifierProcessor.isOldDependencyFile(aarOrJarFile)) {
return listOf(aarOrJarFile)
}
// 情况 3: 如果在黑名单也不需要处理
if (jetifierBlackList.any { it.containsMatchIn(aarOrJarFile.absolutePath) }) {
return listOf(aarOrJarFile)
}
// 情况 4: 对剩下的库进行处理
val outputFile = File(outputDirectory, "jetified-" + aarOrJarFile.name)
val maybeTransformedFile = try {
jetifierProcessor.transform(
setOf(FileMapping(aarOrJarFile, outputFile)), false
)
.single()
} catch (exception: Exception) {
throw RuntimeException(
"Failed to transform '$aarOrJarFile' using Jetifier." +
" Reason: ${exception.message}. (Run with --stacktrace for more details.)",
exception
)
}
...
return listOf(maybeTransformedFile)
}
}
这里主要看下transform方法,aar或jar可以分为四类:1.AndroidX库 2.老的support库,表示在之前的依赖替换阶段没有被替换 3.黑名单中的其他库 4.非黑名单中的其他库。只对情况4进行处理,最终还是调用了jetifier库中Processor类。备注:我们可以通过在gradle.properties文件中添加android.jetifier.blacklist属性指定不需要处理的黑名单。
Jetifier源码
jetifier库源码地址:https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/support/+/refs/heads/androidx-jetifier-release/jetifier/
创建Processor对象是config的参数值是ConfigParser.loadDefaultConfig()表示加载默认的配置,最终是通过读取default.generated.config文件中的json数据转换为Config对象。
ConfigParser.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22object ConfigParser {
private const val TAG: String = "Config"
private val gson = GsonBuilder().setPrettyPrinting().create()
...
fun parseFromString(inputText: String): Config? {
return gson.fromJson(inputText, Config.JsonData::class.java).toConfig()
}
...
fun loadDefaultConfig(): Config? {
Log.v(TAG, "Using the default config '%s'", Config.DEFAULT_CONFIG_RES_PATH)
// Use getResource().openStream() instead of getResourceAsStream() as the latter can result
// in concurrency issues (see http://issuetracker.google.com/137929327 for details).
val inputStream = javaClass.getResource(Config.DEFAULT_CONFIG_RES_PATH).openStream()
inputStream.reader().use {
return parseFromString(it.readText())
}
}
...
}
default.generated.config文件中存放了support库和androidx库之间的映射关系,通过注释可以看出该文件是由default.config配置文件和preprocessor/scripts/processDefaultConfig.sh脚本生成的,这里不再对该shell脚本进行分析,有兴趣的同学可以自己看下。
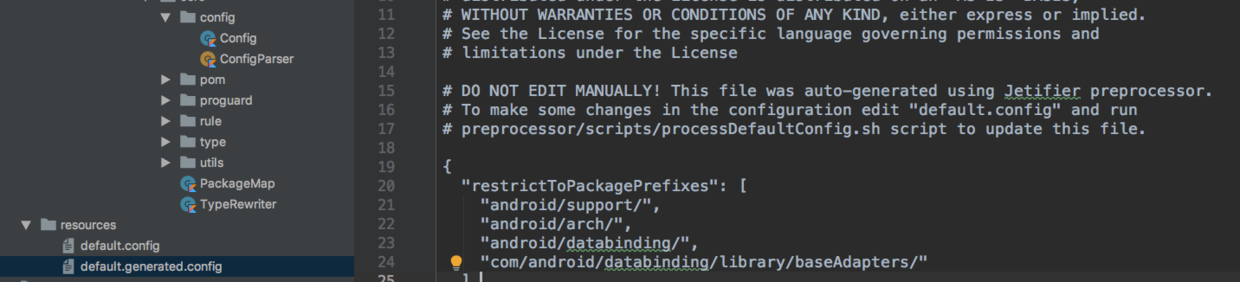
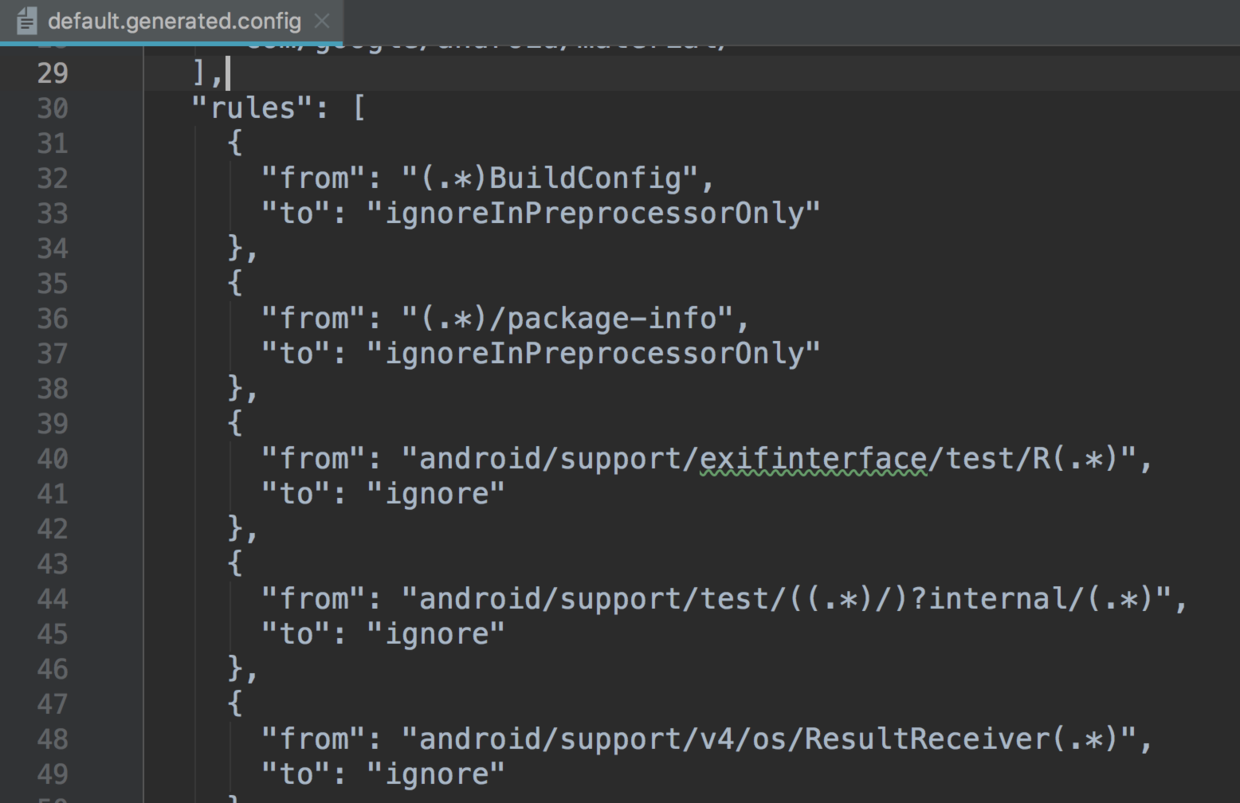
回过头来继续分析Processor的处理,上面注册的JetifyTransform最终调用了Processor的transfrom方法,transform方法已经被废弃,内部调用了transform2方法,这里主要看下transform2方法:
Processor.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80fun transform2(
input: Set<FileMapping>,
copyUnmodifiedLibsAlso: Boolean = true,
skipLibsWithAndroidXReferences: Boolean = false
): TransformationResult {
val nonSingleFiles = HashSet<FileMapping>(input)
for (fileMapping in nonSingleFiles) {
// 将所有文件视为单个文件并检查是否可转换
val file = ArchiveFile(fileMapping.from.toPath(), fileMapping.from.readBytes())
file.setIsSingleFile(true)
val transformer = transformers.firstOrNull { it.canTransform(file) }
if (transformer != null) {
// 单个文件java和xml是可转换的,设置相对路径为输出路径
file.updateRelativePath(fileMapping.to.toPath())
transformer.runTransform(file)
nonSingleFiles.remove(fileMapping)
}
}
if (nonSingleFiles.isEmpty()) {
// 所有文件都是单个文件,处理完成
return TransformationResult(librariesMap = emptyMap(), numberOfLibsModified = 0)
}
val inputLibraries = nonSingleFiles.map { it.from }.toSet()
if (inputLibraries.size != input.size) {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Input files are duplicated!")
}
// 1) 解压并加载所有库文件
val allLibraries = loadLibraries(input)
// 2) 过滤出包含AndroidX 引用的库
val librariesToProcess =
if (skipLibsWithAndroidXReferences) {
filterOutLibrariesWithAndroidX(allLibraries)
} else {
allLibraries
}
// 3) 搜索 POM 文件
val pomFiles = scanPomFiles(librariesToProcess)
// 4) 转换所有 libraries
librariesToProcess.forEach { transformLibrary(it) }
if (context.errorsTotal() > 0) {
if (context.isInReversedMode && context.rewritingSupportLib) {
throw IllegalArgumentException("There were ${context.errorsTotal()} errors found " +
"during the de-jetification. You have probably added new androidx types " +
"into support library and dejetifier doesn't know where to move them. " +
"Please update default.config and regenerate default.generated.config via " +
"jetifier/jetifier/preprocessor/scripts/processDefaultConfig.sh")
}
throw IllegalArgumentException("There were ${context.errorsTotal()}" +
" errors found during the remapping. Check the logs for more details.")
}
// 5) 转换 POM 文件
transformPomFiles(pomFiles)
// 6) 找到签名文件如果需要则抛出异常
runSignatureDetectionFor(librariesToProcess)
val numberOfLibsModified = librariesToProcess.count { it.wasChanged }
// 7) 重新打包到存档文件
var result = allLibraries
.map {
if (it.wasChanged || copyUnmodifiedLibsAlso) {
it.relativePath.toFile() to it.writeSelf()
} else {
it.relativePath.toFile() to null
}
}.toMap()
return TransformationResult(
librariesMap = result,
numberOfLibsModified = numberOfLibsModified)
}
先来分析下主要流程:
0)首先对传入的单个文件包含java和xml做了转换处理,如果列表为空则表示处理完成
1)解压并加载所有库文件
2)根据方法参数值过滤掉包含androidx引用的库,默认不过滤
3)扫描加载所有pom文件
4)转换所有库文件
4.1)判断转换如果发生错误则抛出异常
5)转换所有pom文件
6)找出签名文件如果需要则抛出异常
7)重新打包到存档文件
8)最后返回处理结果
然后来看一下具体的转换细节,其中transformers是一个list包含四个类,分别用于处理字节码class非单个文件、xml非pom文件、proguard非单个文件、单个java源码文件,上面流程首先将传入的所有文件视为单个文件使用JavaTransformer和XmlResourcesTransformer对java源码文件和xml文件进行了处理。第4步使用transformers对所有库文件进行了处理,第5步对所有pom文件进行了处理。
Processor.kt1
2
3
4
5
6private fun createTransformers(context: TransformationContext) = listOf(
ByteCodeTransformer(context),// class && !single
XmlResourcesTransformer(context),// xml && !pom
ProGuardTransformer(context), // proguard && !single
JavaTransformer(context) // java && single
)
不同类型的转换处理相关代码原理一样,都是通过映射关系使用正则匹配等方法进行替换。这里只看下字节码的处理,字节码的处理类ByteCodeTransformer使用了ASM工具对class文件进行了处理并将结果保存在ArchiveFile对象中,在上述流程第7步重新打包到了存档文件中,完成了对第三方库文件的处理。
ByteCodeTransformer.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20class ByteCodeTransformer internal constructor(
private val context: TransformationContext
) : Transformer {
...
override fun runTransform(file: ArchiveFile) {
val reader = ClassReader(file.data)
val writer = ClassWriter(0 /* flags */)
val remapper = CoreRemapperImpl(context, writer)
reader.accept(remapper.classRemapper, 0 /* flags */)
if (!remapper.changesDone) {
file.setNewDataSilently(writer.toByteArray())
} else {
file.setNewData(writer.toByteArray())
}
file.updateRelativePath(remapper.rewritePath(file.relativePath))
}
}
这里使用了ClassRemapper,ClassRemapper是一个使用Remapper重新映射类型的ClassVisitor,这里对Remapper进行了自定义:
CustomRemapper.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52class CustomRemapper(private val remapper: CoreRemapper) : Remapper() {
override fun map(typeName: String): String {
return remapper.rewriteType(JavaType(typeName)).fullName
}
override fun mapPackageName(name: String): String {
return remapper.rewriteType(JavaType(name)).fullName
}
override fun mapValue(value: Any?): Any? {
val stringVal = value as? String
if (stringVal == null) {
return super.mapValue(value)
}
fun mapPoolReferenceType(typeDeclaration: String): String {
if (!typeDeclaration.contains(".")) {
return remapper.rewriteType(JavaType(typeDeclaration)).fullName
}
if (typeDeclaration.contains("/")) {
// Mixed "." and "/" - not something we know how to handle
return typeDeclaration
}
val toRewrite = typeDeclaration.replace(".", "/")
return remapper.rewriteType(JavaType(toRewrite)).toDotNotation()
}
if (stringVal.startsWith("L") && stringVal.endsWith(";")) {
// L denotes a type declaration. For some reason there are references in the constant
// pool that ASM skips.
val typeDeclaration = stringVal.substring(1, stringVal.length - 1)
if (typeDeclaration.isEmpty()) {
return value
}
if (typeDeclaration.contains(";L")) {
// We have array of constants
return "L" +
typeDeclaration
.split(";L")
.joinToString(";L") { mapPoolReferenceType(it) } +
";"
}
return "L" + mapPoolReferenceType(typeDeclaration) + ";"
}
return remapper.rewriteString(stringVal)
}
}
CustomRemapper重写了Remapper的3个方法,分别是map方法用于映射类的内部名称和新名称,mapPackageName方法用于映射包名和新名称,mapValue方法用于映射值。方法内部最终调用了CoreRemapper接口中的rewriteType和rewriteString方法,CoreRemapper的实现类是CoreRemapperImpl:
CoreRemapperImpl.kt1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64class CoreRemapperImpl(
private val context: TransformationContext,
visitor: ClassVisitor
) : CoreRemapper {
...
private val typesMap = context.config.typesMap
var changesDone = false
private set
val classRemapper = ClassRemapper(visitor, CustomRemapper(this))
override fun rewriteType(type: JavaType): JavaType {
val result = context.typeRewriter.rewriteType(type)
if (result != null) {
changesDone = changesDone || result != type
return result
}
context.reportNoMappingFoundFailure(TAG, type)
return type
}
override fun rewriteString(value: String): String {
...
// Try rewrite rules
if (context.useFallbackIfTypeIsMissing) {
val rewrittenType = context.config.rulesMap.rewriteType(type)
if (rewrittenType != null) {
Log.i(TAG, "Map string: '%s' -> '%s' via fallback", value, rewrittenType)
return if (hasDotSeparators) {
rewrittenType.toDotNotation()
} else {
rewrittenType.fullName
}
}
}
// We do not treat string content mismatches as errors
Log.i(TAG, "Found string '%s' but failed to rewrite", value)
return value
}
fun rewritePath(path: Path): Path {
val owner = path.toFile().path.replace('\\', '/').removeSuffix(".class")
val type = JavaType(owner)
val result = context.typeRewriter.rewriteType(type)
if (result == null) {
context.reportNoMappingFoundFailure("PathRewrite", type)
return path
}
if (result != type) {
changesDone = true
return path.fileSystem.getPath(result.fullName + ".class")
}
return path
}
}
方法内部根据条件判断最终调用了映射关系数据Config类获取对应的映射关系完成了转换。
总结
使用本文提供的脚本工具对工程源码迁移到anroidx成本相对较低,迁移到androidx后并非需要对所有依赖库进行升级到对应androidx版本,原因是当我们在gradle.properties文件中添加android.enableJetifier=true属性开启Jetifier后执行打包时会自动将依赖的support库修改为新的androidx库,对于第三方库会对aar中class文件、xml文件以及proguard文件和pom依赖进行处理。
参考
- https://developer.android.com/jetpack/androidx/migrate#migrate
- https://developer.android.com/jetpack/androidx/migrate/class-mappings
- https://github.com/yuweiguocn/MigrateToAndroidX
- https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/support/+/refs/heads/androidx-jetifier-release/jetifier/
- https://github.com/yuweiguocn/build-system

